Hospital bed head units of today and the future
For some years now, hospital bed heads units, driven by the improvement in hospital equipment, have been providing an optimised, intuitive environment in accordance with the space in which they are located
That is to say: they are the perfect complement to hospital beds, forming a block that is designed and installed according to the type of patient who is going to use it and the medical speciality, floor or type of hospital.
In this post, Tedisel would like to talk about the main characteristics of hospital bed head units, their functions, trends in the health sector and what options are available in the market.
What are hospital headboards?
Hospital headboards, far from what they may indicate at first glance, are not the equivalent of the headboard of a normal, typical household bed.
They are part of the hospital bed, yes, but with a different function and design. Specifically, they are the structures, usually arranged vertically or horizontally, which are attached to the wall and are placed precisely on the headboard area of the bed or near the side of the bed.
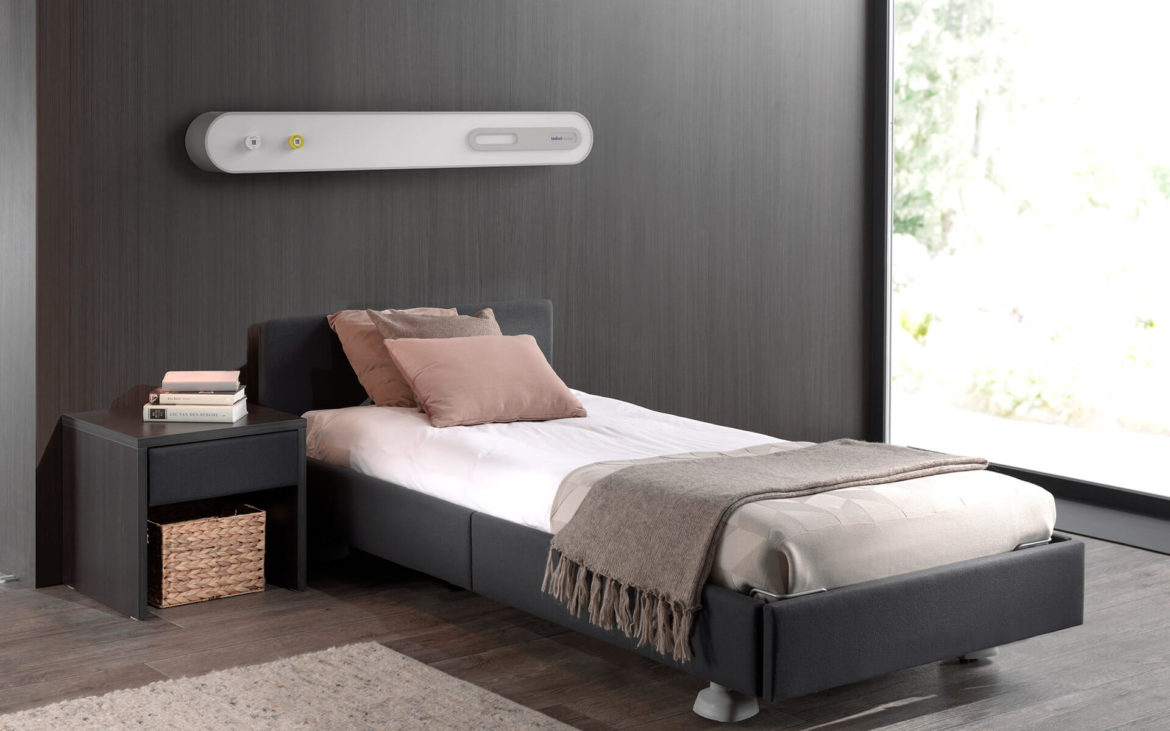

ICARUS Model
What are they for?
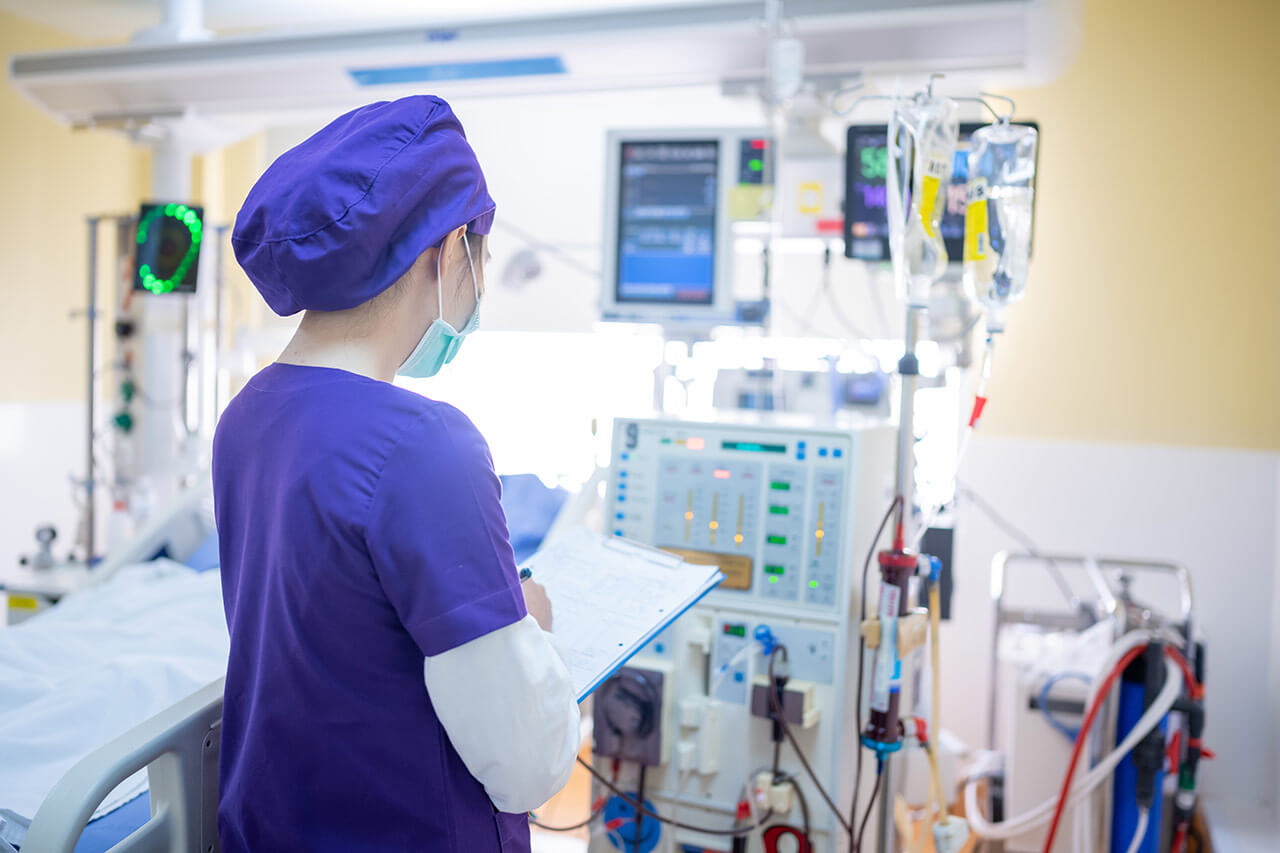
We are referring to those elements that, when we have been patients in a hospital, we have used to warn the nurses of anything. These devices light up indirectly in case someone has to enter or leave the room.
Among their main characteristics is the fact that they have numerous sockets, each with different purposes, but especially electrical, data and gas sockets. On the other hand, we must distinguish between headboards designed for common hospitalisations, or those intended for ICU units, resuscitation rooms, post-operative units, etc. In this case, they are usually more sophisticated.
In any case, they are completely common and necessary elements in hospitals all over the world.
“Among their main characteristics is the fact that they have numerous sockets, each with different purposes, but especially electrical, data and gas sockets.
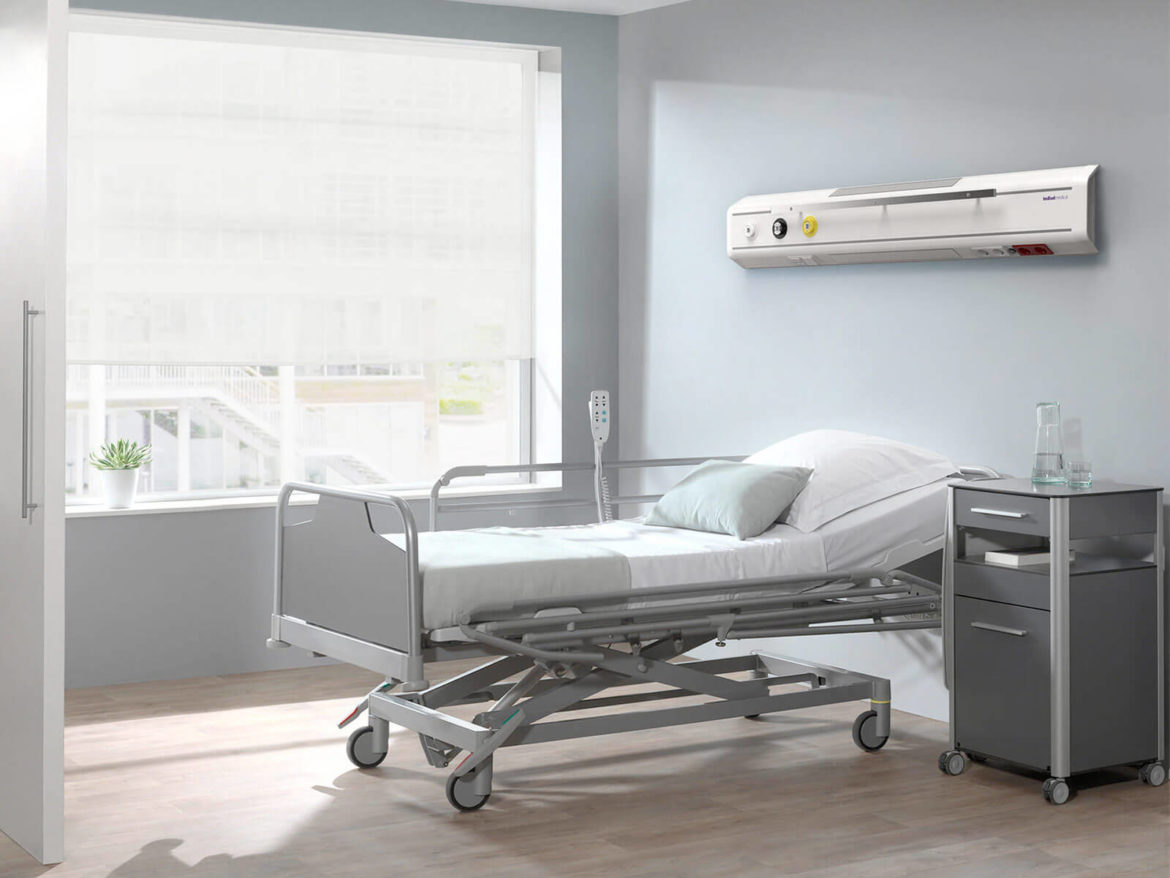

N270 Model
Characteristics and trends in headboards
Hospital bedside cabinets act as devices that have been conceived to provide the physician with close and simple access to supplies needed for therapy. As we said, this is the case of gases, vacuum or electrical energy, fundamentally. In addition, the bedside cabinets provide the patient with ‘extra’ services, such as lighting, alarms or communication systems.
These bed heads form an aesthetically and functionally harmonious whole with the bed, one of the most important parts of the patient unit. The function of the bed in the hospital is to accommodate the patient and has characteristics specifically adapted to his or her ailments. It must always be in perfect condition to ensure that the patient is comfortable, as this is where he or she will spend most of the day during hospitalisation.
Whether headboards are intended for Critical Care services (ICU, ICU, etc.), emergency / resuscitation services, wards of intermediate complexity, or other hospital sectors where their services are required, in the last decade headboards have taken on a new dimension at an aesthetic level, as a whole.
As a result of the greater importance given to the holistic and biophilic experience in hospitals, to the well-being not only of the patient but also of the medical staff, to facilitating their work and the hospitalisation periods of users, headboards have been adapted to blend in with their surroundings. What does this mean? That the type of hospital headboard of yesteryear, useful and efficient but alien to the style of the bed and the room, no longer applies in the new and remodelled hospitals.
Bed heads today are part of a whole: of the bed, of the room, of the type of hospital and of the type of patient. They are oriented and designed specifically for a particular profile, be it paediatric patients, VIP stays, etc.
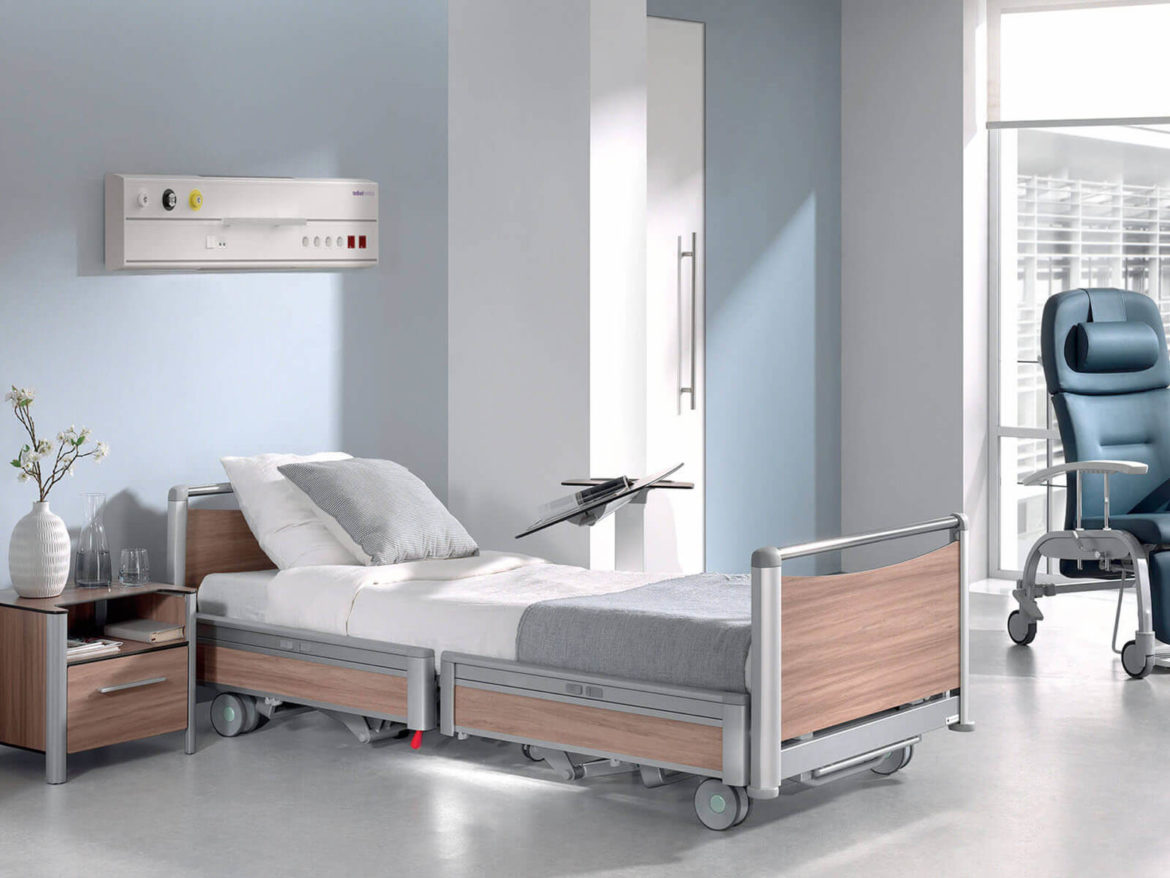
AURA Model
An essential piece of hospital equipment
The hospital bedside goes far beyond the mere hook-up of electrical and diagnostic equipment and the basic functions of lighting, voice recognition and oxygen-enriched gas outlet.
This complex system is continuously being improved to be more omnichannel and adaptive than ever before with a single device. This means that the headboards are intended to facilitate services to all types of patients, from those able to alert the nurse at the push of a button to those who are intubated, sedated or temporarily immobile.
Solutions such as push-button knob, voice activation, etc. are part of the hardware that takes care of the nurse-patient call. Which is ultimately one of the main functions that is not fixed or that can lead to the most uncertainty.
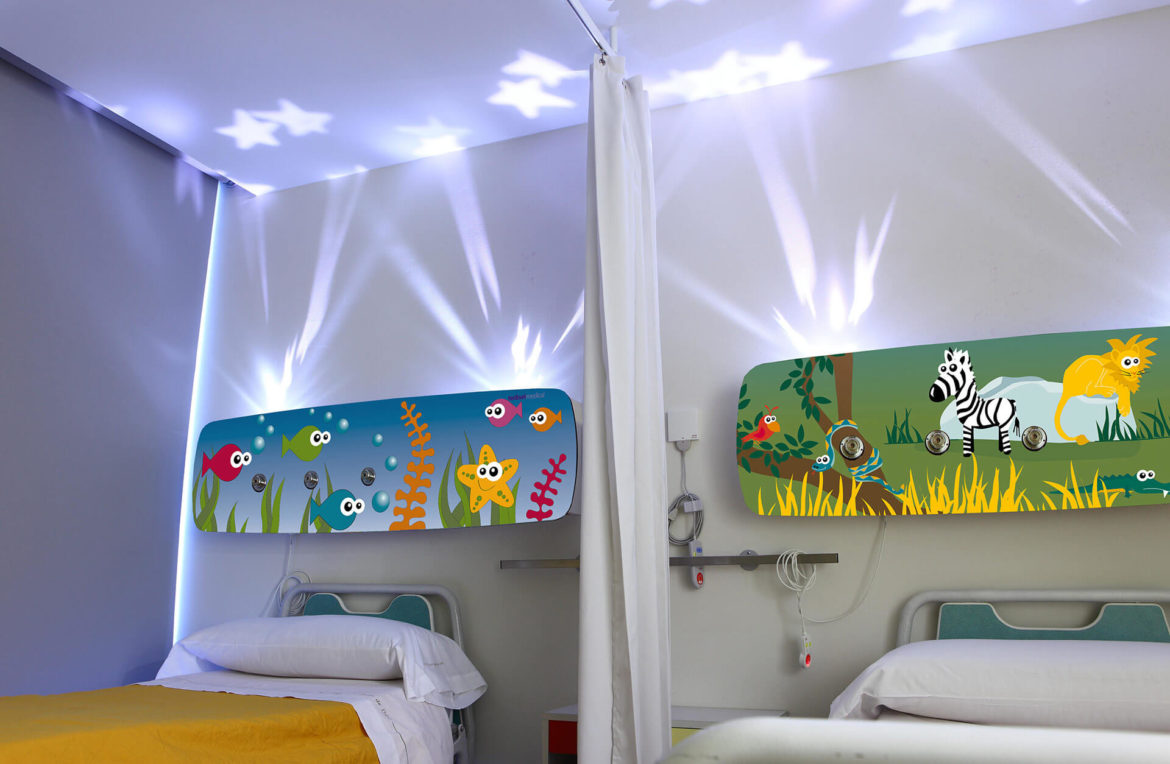

MAYA Model
The most complete catalogue of headboards
In Tedisel Medical we have a wide catalogue of hospital bed heads, integrated wall systems, for all types of patient rooms in hospitals.
Our headboards follow the trend in the health sector of fully integrating the headboard into the room design. Especially in new constructions and remodelling of health centres, this is what is being sought after, both for aesthetic reasons and for simplicity and ease. In short, headboards are elements that offer a very important service, that influence the well-being and recovery of the patient, and that are increasingly integrated at an aesthetic and formal level.
Among our headboards, the following stand out:
Aura
Our modular bed head
It can be customised to adapt to the needs of different areas: hospitalisation, critical areas, operating theatres, etc. It is the perfect equipment to hold different accessories. From a simple rail to a complete sliding system with infusion pumps and trays.
Monobloc bed head
Our best known model in the world, the most sold and installed in thousands of projects; optimal for hospitalisation and general care areas.
Adonis
Known for its design and high load capacity, this is the optimal solution for confined spaces especially in critical areas. It can also serve two beds simultaneously in any area. Adonis allows multiple configurations, depending on the needs of the area where it is to be installed. Its structure integrates two tubes for the placement of various accessories.
Icarus
It is an attractive and futuristic headboard. Its innovative design is mainly customised for hospitalisation and VIP.
Maya
With the little ones in mind, Maya is our paediatric bed head created to provide a cosier and more pleasant space to facilitate the stay of the little ones in hospital.
Ais
Artistic bed head
A bed head, which allows you to customise the front to give a more welcoming atmosphere to the area where you want to install it: maternity, paediatrics, hospitalisation, VIP, etc. Ais, with a minimalist and clean design, allows the placement of accessories by means of a technical rail to the wall.
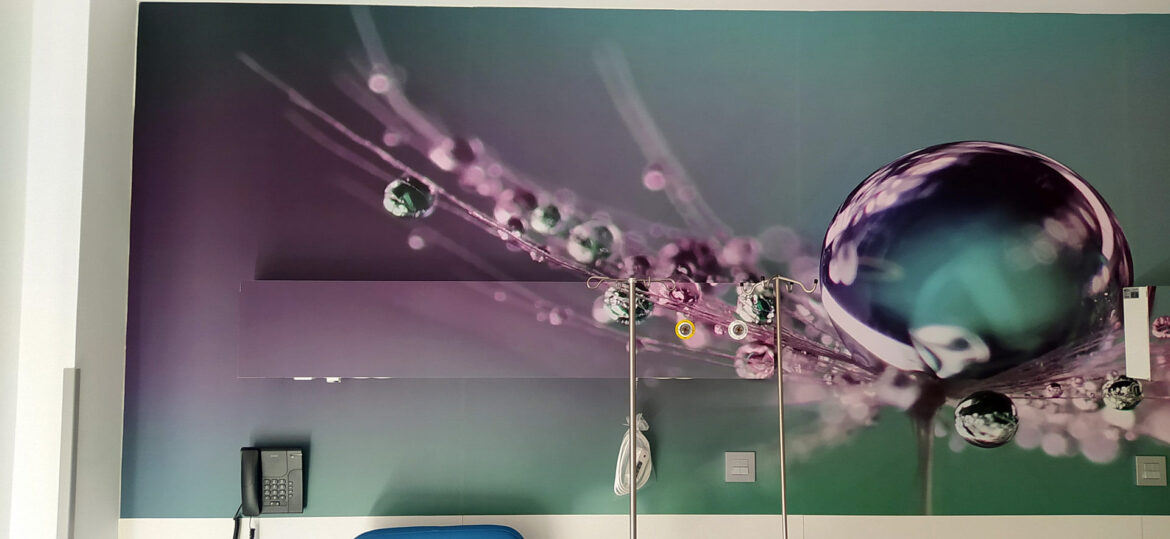
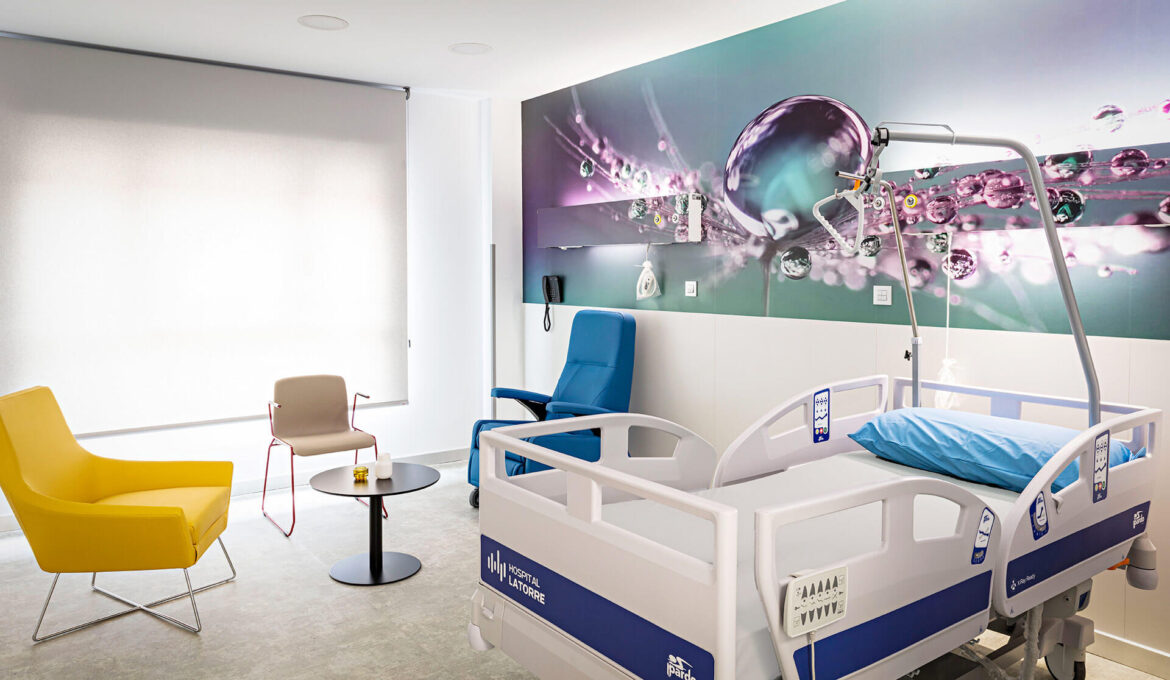
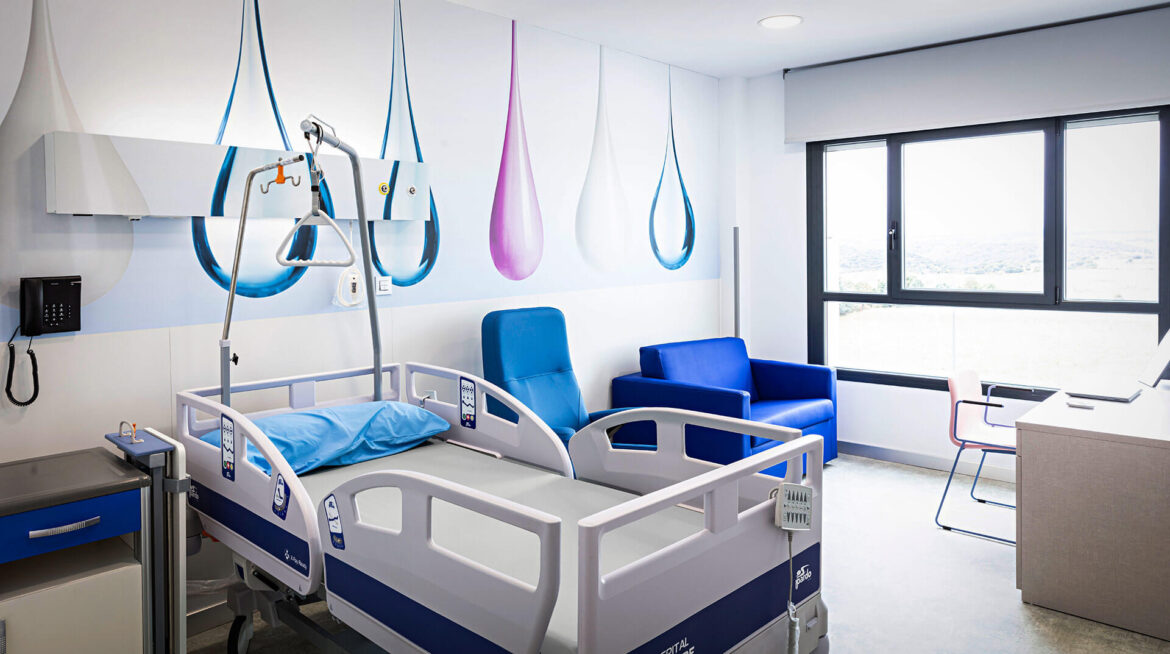
Our latest project with AIS bed head
One of our latest projects is the installation of the AIS model in the Latorre Hospital, in Soria. This bed head with customisable front was integrated 100% at design level in the decorative wall vinyl of the room.
The AIS model adds an architectural touch. It allows you to customize the front to give a cosier atmosphere to the area where you want to install it: Maternity, Paediatrics, Hospitalisation, VIP, etc. Among its features, it stands out for its minimalist and clean design, allowing the placement of accessories by means of a wall-mounted technical rail, such as infusion pumps and IV pole holders, trays and drawers, monitor support arms, examination lamps or medical baskets, among others.