7 hospital energy development trends in 2024
Hospital energy development trends in 2024 are following, and will follow, a very clear pattern: exploiting the potential of the accelerated process of digitalization that the healthcare sector has been undergoing in recent years.
Technology is more than ever the key to providing optimal, improved and higher quality medical care.
This digital transformation is having a major impact on healthcare from all points of view.
Among other things, it allows medical institutions to simplify a wide range of administrative processes and increase their operational efficiency, resulting in benefits both for the management itself and for patients and their families.
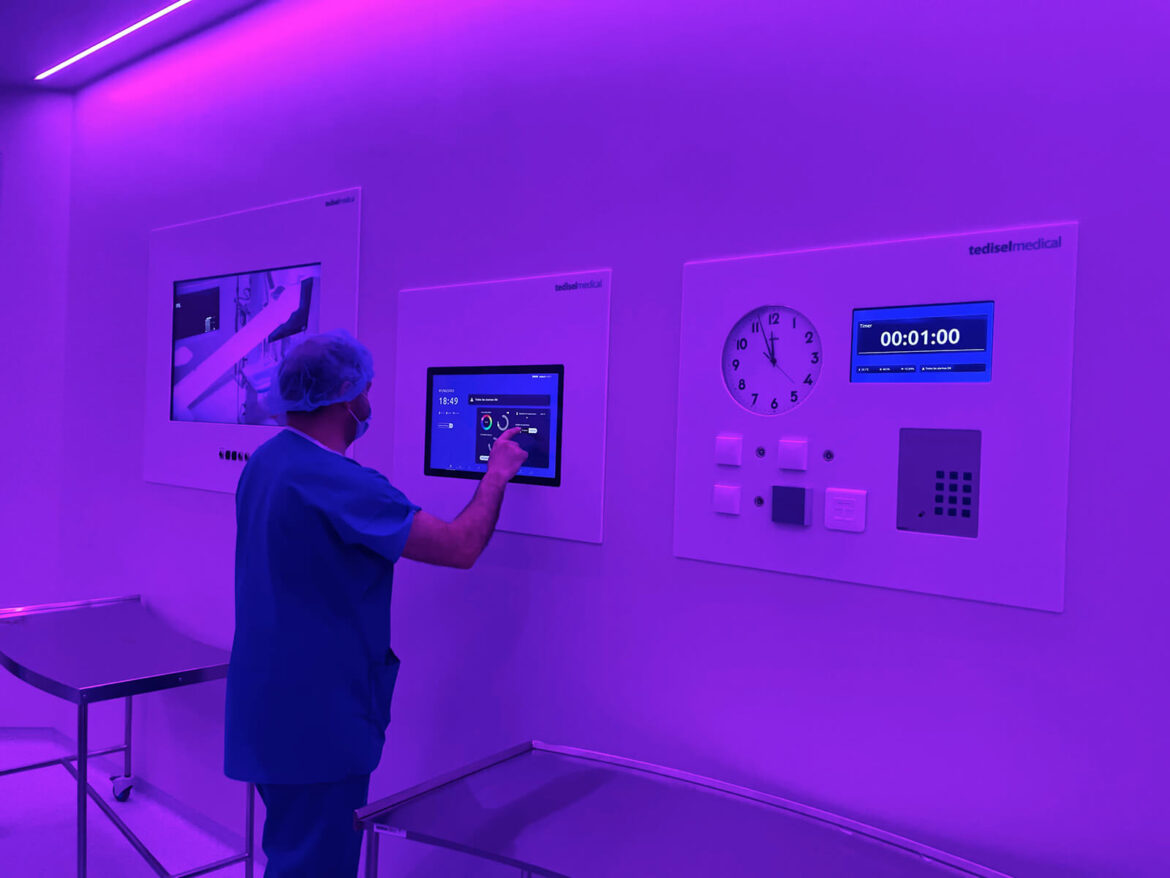
The sector is taking giant steps towards the integration of technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), data analysis and the use of Internet-connected devices. New systems are also driving new hospital energy development on various fronts. Let’s see which are the most interesting in 2024.
1. Increased use of renewable energy
Hospitals can adopt solar, wind or biomass technologies to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels and reduce their carbon emissions.
For example, we are already seeing the implementation of metering and AI models that automate the placement and configuration of power grid components to optimize energy efficiency.
In this regard, the historic agreement reached by nearly 200 countries at COP28 to move away from fossil fuels requires an upgrade and digitization of global energy systems. And the healthcare sector is one of the parties most involved and with the greatest scope.
The goal is for the healthcare sector to stop being the ‘fifth most polluting country’.

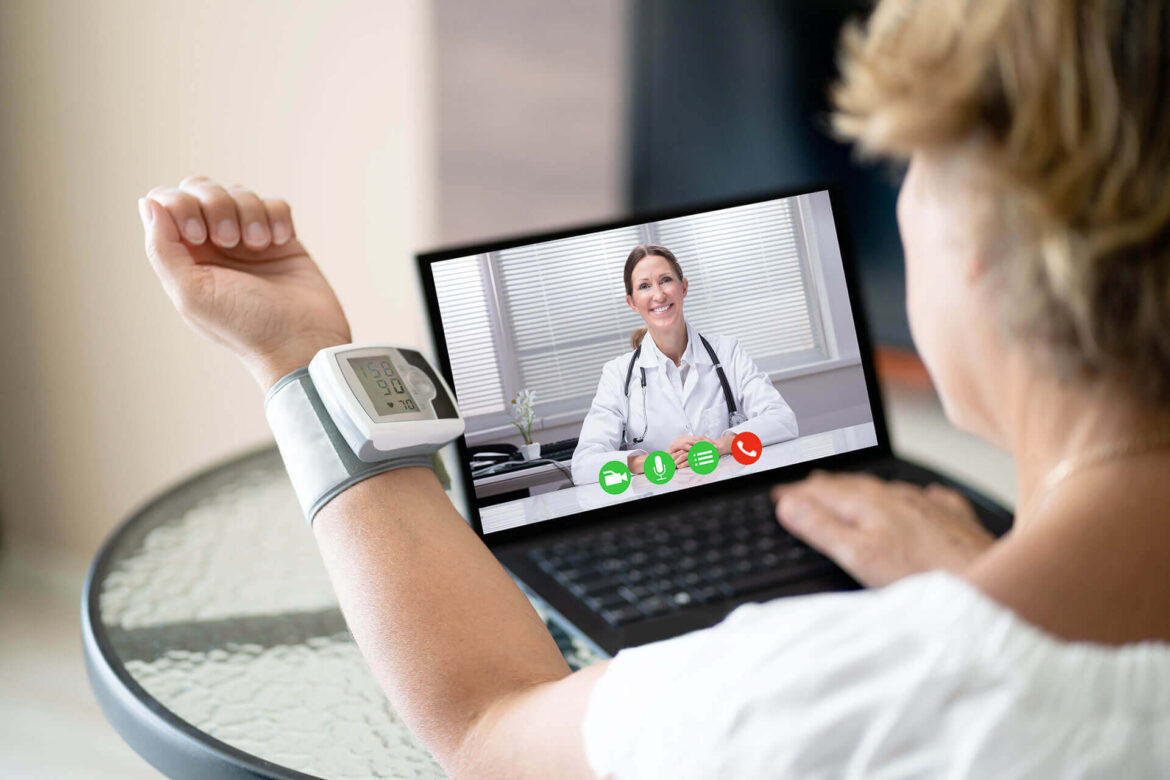
2. The rise of telemedicine
According to Statista projections, it is estimated that by 2025, the global telemedicine market will reach 278 billion dollars.
It is a cutting-edge and essential tool to support the work of healthcare professionals, as well as the operation of medical institutions.
With telemedicine, we reduce congestion in doctors’ offices and hospitals and minimize unnecessary travel, among other benefits.
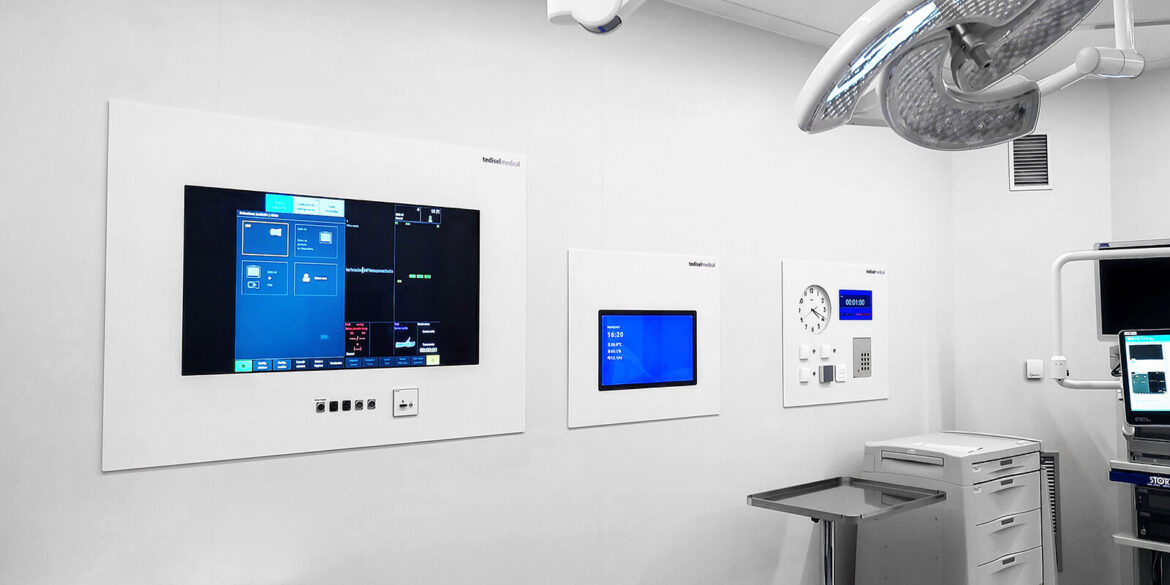
3. Smart Hospitals powered by IoMT
As the adoption of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) increases, healthcare professionals can make use of more devices that enable continuous monitoring of health parameters, remotely and in real time.
This facilitates chronic disease management and contributes to the prevention and early detection of complications.

4. Energy Efficiency
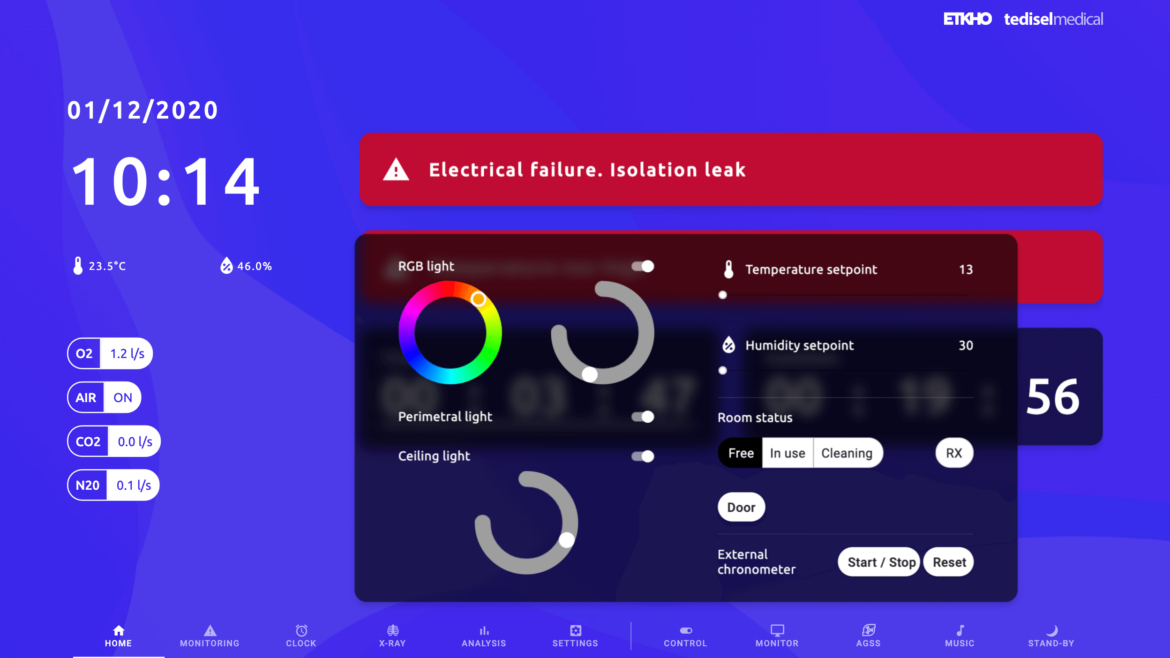
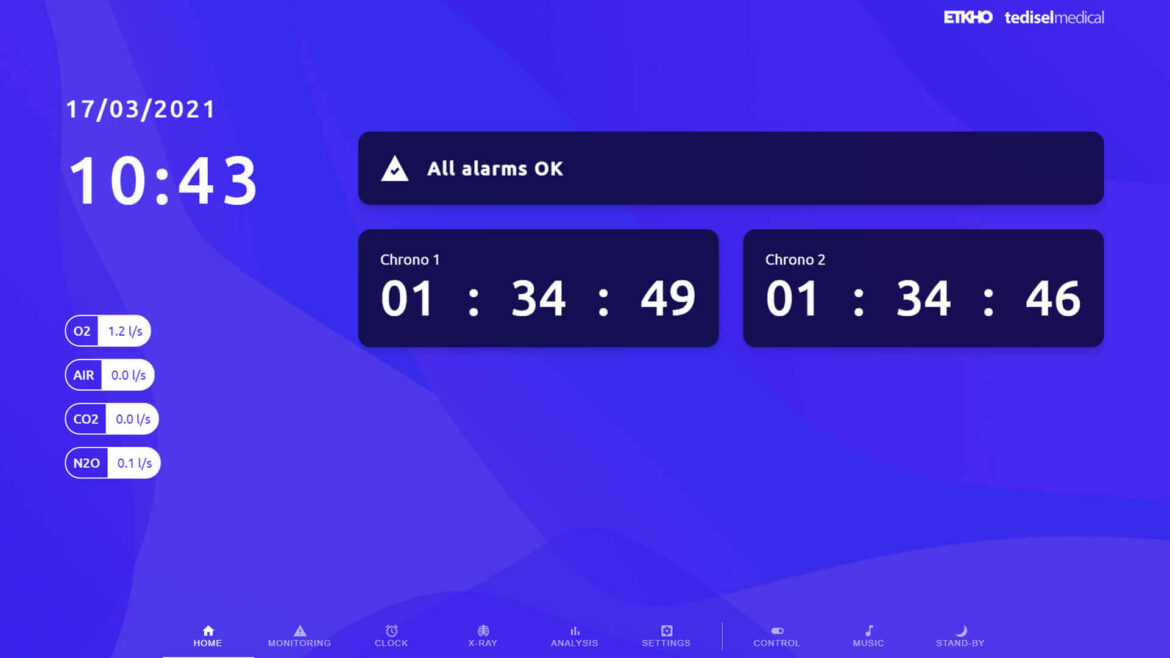
Hospitals seek to improve energy efficiency by upgrading equipment, integrating energy storage batteries, optimizing heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, and adopting smart technologies for energy control and monitoring.
They can also develop microgrids to more efficiently manage locally generated energy and coordinate energy load to optimize resource use.
5. Integration of green energy technologies
The adoption of innovative technologies such as geothermal energy, cogeneration and small-scale hydropower could increase, especially in areas where these energy sources are viable.

6. Focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility
Growing awareness of environmental impact is leading hospitals to prioritize sustainability in their operations, including waste reduction, recycling, and the implementation of eco-friendly practices throughout the institution.
7. Digital avatars and chatbots
Both virtual assistants and chatbots based on Generative AI algorithms have become powerful tools that support the work of medical specialists.
By training AI models with medical literature, practitioners can obtain recommendations on treatments, diagnoses and medications, which influences clinical decision-making.
In sum, these hospital energy development trends in 2024 reflect a move toward greater energy self-sufficiency, a reduced carbon footprint, and greater resilience in hospital infrastructure from the drive for AI, data analytics, and improved medical management and equipment.